What are the Most Common 3D Printing Materials?
Hello everyone, welcome to our 3D Printing guide!! Today in this series of blog we are going to discuss about the materials used for 3D Printing.
With 3D printing, you can make different prototypes and mass-produce parts for a wide range of uses quickly and at a very low cost. But picking the right 3D printing method is only half of the story. In the end, it will be mostly up to the materials to let you make parts with the mechanical properties, functional properties, or looks you want. First we will discuss about the different plastic materials that we can use to print the objects.
Plastic:
Most of the 3D printing process is done with plastic material, even though there are other materials that can be used. Plastic is very useful and can be used for many things. Material for 3D printing with plastic comes in many different colours and can also be clear. Most of the time, 3D printing filaments are sold on spools that are either shiny or dull.
Plastic is a popular 3D printing material because it can be moulded into a wide range of shapes, is durable, smooth, and comes in different colours. In addition, plastic is less expensive than other materials for 3D printing. Fused deposition modelling is the most widely used technique for 3D printing plastic (FDM).
Plastics such as Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (abbreviated as ABS), Polylactic Acid (abbreviated as PLA), Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (abbreviated as PETG), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (abbreviated as TPU), High Impact Polystyrene (abbreviated as HIPS) and Nylon, etc are among the most frequently used plastics.
1. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS):
ABS has been used in 3D printing for a long time. It is one of the first plastics to be used in industrial 3D printers. Even though it has been around for a long time, ABS is still a very popular material because it is cheap and has good mechanical properties such as Heat Resistant, Impact Resistant and Rigid. This means that you can use it to print parts that will last even after a lot of use and wear.
In order to get the best ABS prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 95-110 °C
- Build Surface: Use Kapton Tape or use ABS slurry.
- Extruder Temperature: 220-250 °C
ABS material can be used in case of Functional prototypes.
2. Polylactic Acid (PLA):
One of the most common materials used in home 3D printing is polylactic acid, or PLA for short. Due to its low printing temperature and lack of need for a heated bed, it has become the standard filament for extrusion-based 3D printers. If you're just getting started with 3D printing, PLA is a fantastic option because it's simple to work with, it's cheap, and it yields functional parts for a wide range of projects. It's also one of the environmental friendly filaments for the planet that you can buy right now.
Hardware Requirements:
In order to get the best PLA prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 45-60 °C (Sometimes Heated Bed is not required)
- Build Surface: Use Painter's Tape, PEI, Glass plate and Glue stick.
- Extruder Temperature: 190-220 °C
- Cooling: Fan Speed: 100%
PLA material can be used in case of Concept models & Looks-Like prototypes.
3. Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG):
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) water bottles are made from PETG, a glycol-modified form of PET. It has decent impact resistance for a semi-rigid material, but its softer surface makes it more wear-prone. Plastics made from this material cool quickly and with almost no warping. It is Chemically Resistant, Fatigue Resistant, and also a Water Resistant material.
In order to get the best PETG prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 75-90 °C
- Build Surface: Use Painter's Tape and Glue stick.
- Extruder Temperature: 230-250 °C
- Cooling: Fan Speed: 10-100%
PETG material can be used in case of Waterproof applications & Snap-fit components.
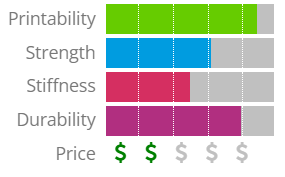
4. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): (Referred as Flexible Material)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), a hybrid of hard plastic and rubber, are used to create flexible filaments. Elastic plastic is exactly what it sounds like: plastic that can be easily bent and stretched. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is the most popular type of TPE used in 3D printing filaments, though there are many others. It is Flexible and Fatigue Resistant material.
Hardware Requirements:
In order to get the best TPU prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 45-60 °C
- Build Surface: Use Painter's Tape and PEI.
- Extruder Temperature: 225-245 °C
- Cooling: Fan Speed: 10-100%
TPU material can be used in case of Flexible prototypes & Vibration damping applications.
5. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS):
HIPS, or High Impact Polystyrene, is a dissolvable support material commonly used in combination with ABS. When used as a support material, HIPS can be dissolved in d-Limonene, removing any markings caused by support removal from your print. Because HIPS has many of the same printing properties as ABS, it is an obvious dual extrusion partner. Not only is HIPS excellent for supporting your ABS prints, but it is also more dimensionally stable and slightly lighter than ABS, making it an excellent choice for parts that will be worn out or used in applications where the lighter weight is advantageous.
In order to get the best HIPS prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 100-115 °C
- Build Surface: Use Kapton Tape, PEI, Glass Plate and Glue stick.
- Extruder Temperature: 230-245 °C
- Cooling: Fan (Not Required)
HIPS material can be used in case of support, Cosplay & Wearables.
6. Nylon:
Nylon (also known as polyamide) is a common plastic because of its durability and malleability. Some brands of nylon filament can be printed at temperatures as low as 220 °C, despite the fact that most require extruder temperatures near 250 °C. These lower-temperature variants can be useful and may prevent you from having to upgrade your hotend, as many printers do not come with a hotend that can safely reach 250 °C. Because of the many print quality issues that arise when printing with Nylon that has absorbed moisture, proper filament storage is crucial.
Hardware Requirements:
In order to get the best Nylon prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 70-90 °C
- Build Surface: Use PEI and Glue stick.
- Extruder Temperature: 225-265 °C
- Cooling: Fan (Not Required)
Nylon material can be used in case of Functional prototypes & Wear resistant parts.
So, these are some of the most usable plastic materials in 3D printing. Now we will see some more materials used for 3D printing.
7. Metal Filled:
Filaments that are "metal filled" are loaded with a fine metal powder, usually one of the following: Copper, Bronze, Brass, or Stainless Steel. Depending on the producer, each filament may have a different amount of metal powder infused into it. The filament is significantly heavier than typical plastics due to the presence of this metal powder. Because of this, even though the settings and amount of material used are identical, the printed parts made from metal-filled PLA will be significantly heavier. As they pass through the hotend, metal-filled filaments can be very abrasive.
Hardware Requirements:
In order to get the best prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 45-60 °C
- Build Surface: Use Painter's Tape, PEI and Glue stick.
- Extruder Temperature: 190-220 °C (Hardened Steel Nozzle)
- Cooling: Fan Speed: 10-100%
Metal Filled material can be used in case of Sculptures, Replicas for Museums & Jewellery.
8. Wood Filled:
Wood-based filaments are typically a composite of a PLA base material and various powdered wood derivatives like wood dust or cork. Depending on the manufacturer, the filament may contain anywhere from 10% to 70% wood particles. The appearance of real wood in the 3D printed parts is achieved by the incorporation of these particles. Since wood particles are much softer than carbon fibres or metal, this filament is also less abrasive than other composite filaments.
Hardware Requirements:
In order to get the best prints, you have to make sure that your 3D printer should meet these hardware requirements as below:
- Bed Temperature: 45-60 °C
- Build Surface: Use Painter's Tape, PEI and Glue stick.
- Extruder Temperature: 190-220 °C
- Cooling: Fan Speed: 10-100%
Wood Filled material can be used in case of Household decorations, Toys, etc.
9. Graphene:
In the last few years, research has been going on the different 3D printing materials, and Graphene is one of them. The combination of graphene's conductivity, flexibility, and strength has made it a popular material. The flexibility of this 3D printing material makes it ideal for components of electronic devices like touchscreens. Graphene is also being incorporated into solar panels and building materials. Graphene's light weight and high strength and adaptability make it useful in many different fields.
10. Composite Materials:
Composite materials for 3D printing come in different forms, such as filaments and powders. These materials are good because they are strong, stable, and have the right amount of strength for their weight. Composite fibres are very light, so they can give a part a lot of strength without making it heavier. Composite materials made for engineering-grade 3D printing are also used in place of metal materials.When it comes to selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing, nylon is the base material used for composite powders. Carbon fiber is a type of composite material utilized in 3D printing as an outer coating over plastic materials. These outer coatings of carbon fiber make the plastic stronger.




















Comments
Post a Comment